Industrial equipment failure isn’t just an inconvenience—it’s a financial catastrophe waiting to happen. A single unplanned shutdown can cost manufacturing facilities upwards of $50,000 per hour, while electrical failures in commercial buildings can result in devastating fires, costly OSHA fines, and liability claims that reach into the millions. Yet most facility managers are still operating blind, relying on outdated maintenance schedules and hoping their critical systems won’t fail.
The solution lies in technology that’s been hiding in plain sight: infrared thermal imaging. What was once considered a specialized tool for select industries has evolved into the cornerstone of modern predictive maintenance, offering unprecedented visibility into equipment health and transforming how forward-thinking organizations protect their assets.
The Evolution of Thermal Imaging: From Military to Mainstream
Thermal imaging technology has undergone a remarkable transformation. Originally developed for military applications, today’s commercial thermal cameras feature high-resolution sensors capable of detecting temperature variations as small as 0.1°C. The latest generation of infrared cameras combines advanced sensor technology with AI-powered analytics, wireless connectivity, and cloud-based data management systems.
The thermal imaging market, valued at $7.69 billion in 2024, is projected to reach $16.29 billion by 2034—a testament to its growing adoption across industries. This growth is driven by technological breakthroughs that have made thermal imaging more accessible, accurate, and actionable than ever before.
The Science Behind Early Detection
Every piece of equipment tells a thermal story. Electrical connections generate heat signatures that intensify before failure. Mechanical components show elevated temperatures due to friction, misalignment, or bearing wear. Building envelopes reveal moisture intrusion and insulation degradation through distinctive thermal patterns.
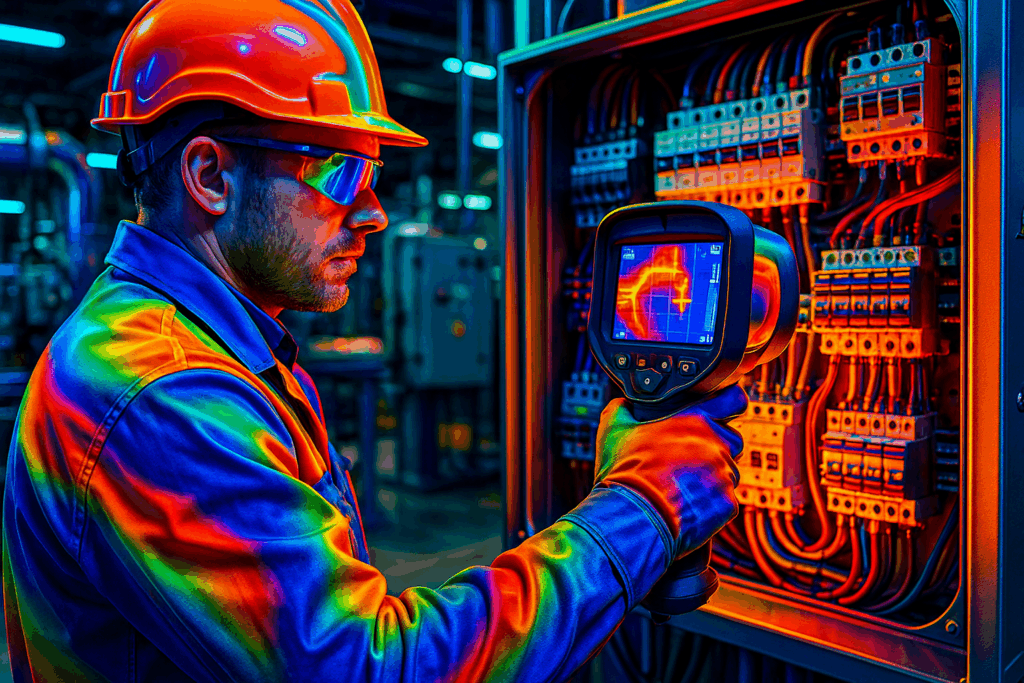
Infrared thermal scanning works by detecting and measuring infrared radiation emitted by all objects above absolute zero. Advanced thermal cameras convert this radiation into detailed temperature maps, revealing hot spots and anomalies invisible to the naked eye. This non-contact methodology allows for safe inspection of energized electrical systems and operating machinery without disrupting operations.
What makes modern thermal imaging particularly powerful is its ability to detect problems weeks or months before traditional inspection methods. A loose electrical connection, for instance, will show elevated temperatures long before it causes a visible arc flash or complete system failure.
Real-World Impact: Quantifying the ROI
The financial benefits of implementing thermal imaging for predictive maintenance are substantial and well-documented. Organizations utilizing thermal scanning report:
- 30-40% reduction in overall maintenance costs compared to traditional reactive approaches
- Up to 50% decrease in unplanned downtime through early problem detection
- 8-12% cost savings over preventive maintenance schedules
- ROI realization within 12-18 months of program implementation
A recent case study from a major manufacturing facility demonstrates these benefits in action. The facility’s thermal imaging program identified a critical motor bearing issue three months before predicted failure. The proactive replacement during scheduled downtime cost $8,000, preventing an estimated $150,000 in emergency repairs and production losses.
Similarly, a commercial office complex avoided a potential electrical fire when thermal scanning revealed overheating in a main distribution panel. The $3,500 repair prevented what could have been millions in fire damage, business interruption, and potential legal liability.
Technology Advancements Reshaping the Industry
The latest generation of thermal imaging technology incorporates several breakthrough features that enhance accuracy and usability:
AI-Powered Pattern Recognition
Modern thermal cameras equipped with artificial intelligence can automatically identify potential failure patterns with over 90% accuracy. These systems learn from historical data, reducing false positives and providing more reliable diagnostics.
Cloud-Based Data Management
Integrated cloud platforms enable centralized monitoring of multiple facilities, automated report generation, and trend analysis across entire facility portfolios. This capability is particularly valuable for organizations managing diverse geographic locations.
Drone Integration
Unmanned aerial vehicles equipped with high-resolution thermal cameras can inspect hard-to-reach equipment, rooftop systems, and large industrial installations quickly and safely. This technology has proven 75% faster and 45% more cost-effective than traditional manual inspections.
IoT Sensor Integration
Thermal imaging systems now integrate with Internet of Things (IoT) sensors, creating comprehensive monitoring networks that provide continuous equipment health insights rather than point-in-time snapshots.
Regulatory Drivers: NFPA 70B and Beyond
The regulatory landscape has significantly strengthened the case for thermal imaging adoption. The 2023 revision of NFPA 70B now mandates annual infrared inspections for all electrical equipment, making thermal scanning a compliance requirement rather than an optional best practice.
Key NFPA 70B requirements include:
- Annual infrared inspections of all electrical equipment
- Comprehensive documentation including thermographer credentials, equipment specifications, and environmental conditions
- Detailed reporting of temperature differentials (ΔT values) and recommended corrective actions
- Priority classification system for identified anomalies
Non-compliance with these standards can result in OSHA citations, insurance claim denials, and significant legal liability in the event of electrical incidents. Forward-thinking facility managers are viewing thermal imaging not just as a maintenance tool, but as essential risk management infrastructure.
Industry-Specific Applications
Thermal imaging applications vary significantly across industries, each presenting unique challenges and opportunities:
Manufacturing and Industrial Production
- Electrical panel monitoring to prevent arc flash incidents and production disruptions
- Motor and bearing analysis for rotating equipment reliability
- Process equipment monitoring including heat exchangers, furnaces, and kilns
- Steam system evaluation for energy efficiency optimization
Healthcare Facilities
- Critical system redundancy verification for life safety equipment
- HVAC system optimization for patient comfort and infection control
- Backup power system reliability for emergency preparedness
- Medical equipment monitoring for specialized temperature-sensitive devices
Data Centers
- Server rack temperature monitoring for optimal cooling efficiency
- UPS and electrical distribution analysis for power reliability
- Cooling system performance evaluation for energy optimization
- Hot spot identification for load balancing and capacity planning
Commercial Real Estate
- Building envelope assessment for energy efficiency improvements
- HVAC system optimization for tenant comfort and operational costs
- Electrical system safety verification for liability protection
- Moisture detection for preventing structural damage
Implementation Best Practices
Successful thermal imaging programs require strategic planning and professional expertise. Key implementation considerations include:
Equipment Selection
High-resolution thermal cameras with appropriate temperature ranges and sensitivity levels are essential for accurate diagnostics. Professional-grade equipment provides the image quality and measurement accuracy necessary for reliable analysis.
Qualified Personnel
Certified thermographers possess the training and experience necessary to interpret thermal images accurately, distinguish between critical and non-critical anomalies, and provide actionable maintenance recommendations.
Baseline Documentation
Establishing thermal baselines for critical equipment enables trend analysis and helps distinguish between normal operational variations and developing problems.
Integration with Maintenance Systems
Thermal inspection data should integrate with computerized maintenance management systems (CMMS) for comprehensive asset tracking and work order generation.
Regular Inspection Cycles
Consistent inspection schedules ensure early problem detection while accommodating operational requirements and regulatory compliance needs.
Looking Forward: The Future of Thermal Diagnostics
As we advance into 2025 and beyond, several trends are shaping the future of thermal imaging in predictive maintenance:
Enhanced AI Capabilities: Machine learning algorithms will become increasingly sophisticated, providing predictive analytics that forecast equipment failures months in advance rather than simply identifying current anomalies.
Automated Inspection Systems: Permanently installed thermal monitoring systems will provide continuous equipment surveillance, alerting maintenance teams to developing problems in real-time.
Augmented Reality Integration: AR-enabled thermal cameras will overlay maintenance instructions and historical data directly onto equipment views, enhancing technician capabilities and reducing inspection time.
Quantum Sensor Technology: Next-generation sensors will provide even greater sensitivity and accuracy, enabling detection of increasingly subtle temperature variations.
The Strategic Imperative
In an era where operational efficiency and regulatory compliance are paramount, thermal imaging has evolved from a nice-to-have capability to an essential business tool. Organizations that embrace this technology position themselves for:
- Reduced operational risk through early problem detection
- Enhanced regulatory compliance with NFPA 70B and safety standards
- Improved financial performance through optimized maintenance spending
- Competitive advantage through higher equipment reliability and uptime
The question for facility managers is no longer whether to implement thermal imaging, but how quickly they can deploy this technology to protect their assets and operations. As equipment becomes more complex and downtime costs continue to rise, the organizations that invest in advanced predictive maintenance capabilities will be the ones that thrive in an increasingly competitive marketplace.
The future of predictive maintenance is already here—it’s infrared, it’s intelligent, and it’s indispensable. The only question remaining is whether your organization will lead this transformation or be left behind by competitors who recognize the strategic value of seeing the invisible.